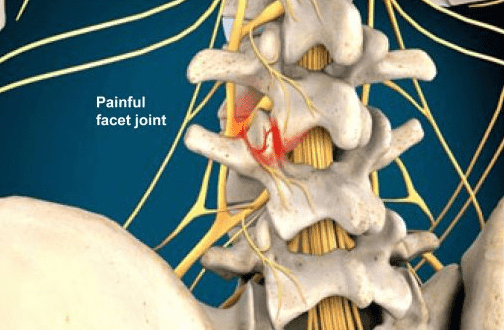
A Medial Branch Block (MBB) is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to treat pain that originates from the facet joints in the spine. The facet joints are small joints located between the vertebrae, and they can become a source of pain due to conditions like osteoarthritis, spinal degeneration, or injury.
Medial Branch Block works by targeting the medial branch nerves, which are small nerves that carry pain signals from the facet joints to the brain. By injecting a local anesthetic (and sometimes a steroid) near these nerves, the procedure temporarily blocks pain signals, helping to confirm if the facet joints are the primary source of pain and providing relief.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA), also known as radiofrequency neurotomy, is a procedure used to treat chronic pain by disrupting the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain. It is often used after a medial branch block has confirmed that facet joints are the source of pain.
RFA uses heat generated by radiofrequency energy to target specific nerves. The procedure is typically done for facet joint pain but can also be used for other types of nerve-related pain.
Medial Branch Block: A diagnostic and short-term pain relief procedure used to confirm that facet joints are the source of pain. It involves a temporary anesthetic injection and is often used as the first step before considering other treatments.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): A longer-lasting, therapeutic procedure that disrupts the pain signals of the nerves, providing long-term pain relief (months to years). It is typically used after a medial branch block has confirmed that the facet joints are the source of pain.
We will do our best to accommodate your busy schedule. Request an appointment today!
Mon-Fri: 9am-5pm