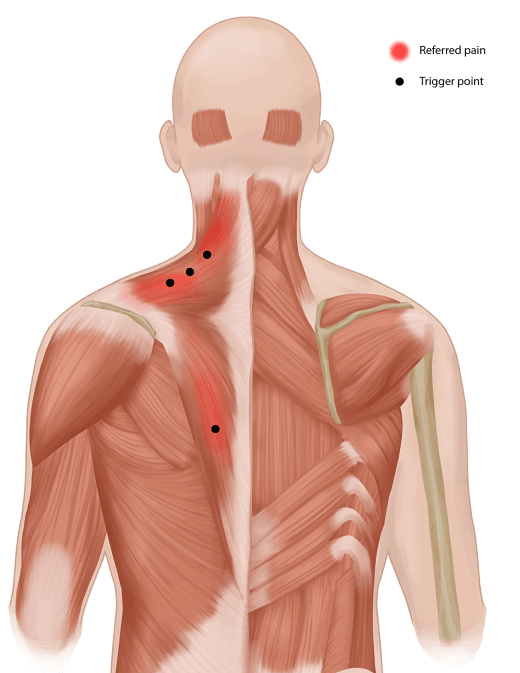
A Trigger Point Injection (TPI) is a medical procedure used to treat muscle pain and muscle spasms, particularly those associated with myofascial pain syndrome. This syndrome occurs when trigger points—tight, painful areas of muscle—develop within a muscle or its fascia (the connective tissue surrounding muscles). Trigger points can cause localized pain, referred pain (pain felt in another part of the body), and muscle stiffness.
A trigger point injection involves injecting medication, typically a local anesthetic, sometimes combined with a corticosteroid or botulinum toxin (Botox), directly into the trigger point to relieve pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve muscle function.
A trigger point is a small, tight knot in the muscle that can be felt as a tender lump. These points can develop in response to muscle overuse, stress, injury, or poor posture. The pain from a trigger point may be localized to the area of the knot or may refer pain to other parts of the body.
Trigger point injections are used to provide pain relief and muscle relaxation by injecting medication directly into the trigger points. The procedure involves:
Identification of Trigger Points: The doctor will palpate (feel) the muscle to identify areas of tightness and tenderness where the trigger points are located. These areas are typically characterized by muscle knots.
Preparation: The skin over the target area is cleaned with antiseptic to minimize the risk of infection.
Injection: A fine needle is inserted into the trigger point, and the appropriate medication (local anesthetic, corticosteroid, or Botox) is injected directly into the muscle knot. The anesthetic helps to numb the area, while the corticosteroid (if used) helps to reduce inflammation.
Post-Procedure: After the injection, the muscle may feel sore temporarily, but many patients experience relief from the muscle tension and pain after a few hours to a day. The full effects of the treatment may take several days to become apparent.
Trigger point injections are commonly used for conditions such as:
Though generally safe, trigger point injections can have some side effects and risks:
Trigger point injections are effective for many patients, providing pain relief and improved muscle function. The pain relief from an injection can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months. In some cases, multiple injections may be necessary to provide sustained relief. For chronic or recurrent muscle pain, trigger point injections can be part of a broader pain management strategy, including physical therapy, stretching exercises, and postural corrections.
We will do our best to accommodate your busy schedule. Request an appointment today!
Mon-Fri: 9am-5pm